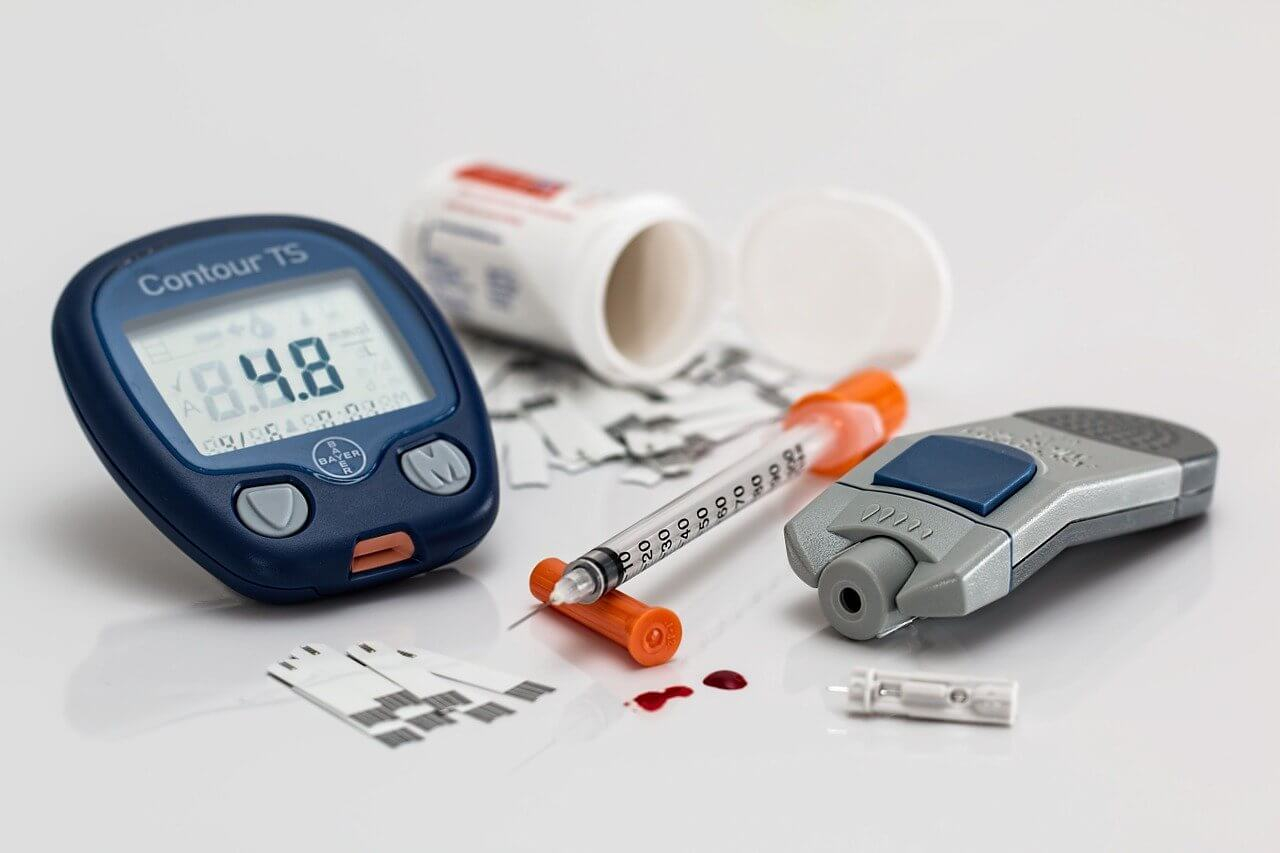
Getting a diagnosis of diabetes can be a pretty scary time in anyone’s life. Before you are able to move forward and start learning how to live with debates, it is important that you take the time you need to understand more about the condition. Learning more about what diabetes is, why it can occur, and how it can present itself can be a critical first step toward effective diabetes management.
What is Diabetes
Diabetes is a form of chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects the way in which your body turns food into energy. When food is consumed, it is then broken down into sugar, otherwise known as glucose, which is then released into your body. When levels of blood sugar in your body rise, a signal is sent to your pancreas to release the hormone insulin, which then triggers a response that allows the blood sugar into your cells to be used as energy.
People who have diabetes have an issue with the way that the body produces or uses insulin. Namely, the body either cannot produce enough insulin or is not able to use the insulin that is produced effectively. Problems with the production or use of insulin cause glucose to remain in the bloodstream. Having too much sugar in your bloodstream can lead to serious health problems over time, such as heart disease, kidney disease, or blindness.
The Different Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes, all of which have slightly different causes. While each type of diabetes is serious, they all can be managed. Using an accurate blood sugar monitor to track your blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine are all vital steps to managing diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes affects between 5 to 10% of the people who have diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is a condition to be caused by an autoimmune reaction that causes your body to stop producing inulin. The onset of symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually occurs in childhood, the teenage years, or early adulthood. None knows the cause of type 1 diabetes, and the condition requires constant insulin intake.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes occurs when your body is not able to use the insulin it produces to keep healthy levels of blood sugar. Type 2 diabetes takes years to develop and tends to affect adults (although it can occur in young children and teenagers). It is possible to spot the signs of prediabetes, and you can prevent or slow down the onset of the condition with the right treatments such as exercise, eating healthy, and lifestyle treatment.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops when a woman is pregnant and can occur in women with no prior history of the condition. While gestational diabetes does tend to go away once the child is born, it can increase the chances of contracting type 2 diabetes in later life. Gestational diabetes can also increase the chances of your child having obesity as a child or teenager, which in turn increases the likelihood of the child developing type 2 diabetes.